By Thomas Benson, education specialist for the Detroit Zoological Society.
As an educator, I am always looking for unique and meaningful ways to engage students in learning about the world around them. So when the opportunity presented itself for me and Jordan Reichenbach, an animal care staff member, to participate in a research project in the Amazon rainforest with the Maijuna indigenous group, we jumped at the chance.
The Maijuna are an indigenous group that has lived in the Sucusari region of Peru for centuries. They have a deep connection to the land, water and animals who call the Amazon home. This deep connection can be seen in their rich cultural heritage and made this trip a life-changing experience.
As part of the research project, in conjunction with OnePlanet, a nonprofit engaged in empowering indigenous communities to build a more sustainable future, and the Detroit Zoological Society, Jordan and I worked alongside the Maijuna to set up trail cameras in the jungle. These cameras capture images of the rich diversity of animals that have re-inhabited the Maijuna ancestral lands after the ejection of loggers, providing valuable data for conservation efforts.
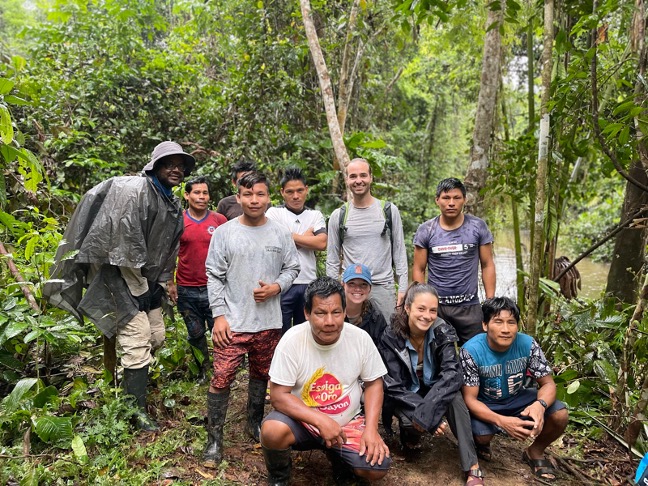

As educators, we sometimes think we have a pulse on every movement and every cause. But truthfully, I had never heard of the type of conservation work, or at least the term used for it, that I was participating in. Biocultural conservation, as I would learn, is where, by helping the indigenous people preserve their culture and way of life, you, in turn, help preserve the ecosystem around them. The Peruvian government’s proposal and effort to construct a road through the heart of Maijuna lands after removing illegal logging undermines this principle and has ignited the passion behind the continuation of the trail camera project. This project aims to help preserve an essential way of life for the Maijuna — hunting — that a road would otherwise destroy. The Maijuna hold hunting as a vital aspect of their cultural heritage and identity. For generations, hunting has provided sustenance, strengthened social bonds and preserved their traditional knowledge. They recognize the importance of sustainable hunting practices and, in turn, employ traditional techniques and closely manage their lands, ensuring the long-term preservation of both their cultural traditions and the biodiversity of the surrounding ecosystem.
In many other countries across the globe, governments are debating the delicate balance between development and environmental preservation. This same issue has pitted the Peruvian government against its indigenous people and conservationists from around the world. Environmental activists, scientists and indigenous groups have joined forces, using the data collected from projects like this one to advocate for sustainable alternatives that prioritize the protection of the Amazon’s fragile ecosystem. They emphasize the need for comprehensive environmental impact assessments, consideration of indigenous rights and investments in alternative modes of transportation and infrastructure that minimize ecological harm.
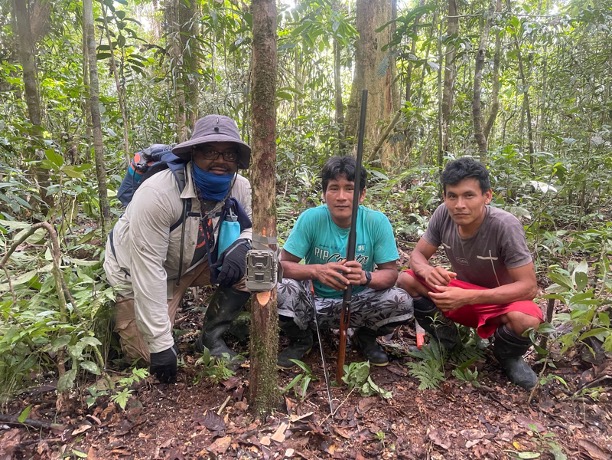

The Amazon rainforest, home to countless plant and animal species found nowhere else on Earth, plays a crucial role in maintaining global climate stability and supporting indigenous communities. Opposition to the road stems from a deep concern about the potentially irreversible damage it could inflict on one of the world’s most biodiverse and ecologically significant regions.
The Peruvian government faces the difficult task of evaluating the potential benefits against the potential consequences while considering the long-term impacts on biodiversity, climate change, and the rights of indigenous communities. The outcome of this ongoing debate will either serve as an example of preservation or as a global reminder of the pressing need to protect and preserve our planet’s invaluable natural ecosystems.
Participating in research in the jungle was a challenging but rewarding experience. The heat and humidity were intense, and there were many bugs and other animals to contend with. However, the Maijuna’s kind and welcoming spirit outweighed any of the negatives. Their willingness to teach us so many aspects of their way of life and the importance of preserving their culture was truly inspiring. Victorino Rios Torres was one of those teachers — his knowledge of the plants and animals of the forest and how his people use them for things from medicine to building houses to spiritual lore were awe-inspiring.

One of the trip’s most memorable moments was when one of the elders and founders of Sucusari, Sebastian “Shebaco” Rios Ochoa, joined us for dinner. During the festivities, he invited all to sit and listen as he recounted the stories of his people. One such story was the origin of the giant river otters who call the Amazon River their home. According to the story,
“One day, a group of people noticed an agua jaula full of fish. They had no idea how the fish got there, and the fish could not escape. So they put some tree sap into the water to kill the fish. All the fish floated to the surface, allowing the group to catch all the fish. But one guy did not think taking the fish was a good idea. He noticed this large tree beginning to shake, along with macaws and other animals calling down to the water as the people gathered the fish. Eventually, the people gathered all the fish and took them back to their homes, where they began preparing them to eat. The one guy, who thought something was wrong, had saved one small fish for himself but forgot to grab it, so he returned to the agua jaula. When he arrived, he was horrified by what he saw; evil spirits were starting to descend out of the tree, so before they saw him, he decided to run back to his people to warn them. But they had already eaten the fish gathered from the agua jaula under this now terrifying tree and had fallen into a deep sleep. He tried everything to wake them, but he could not. As he was trying to wake his people, the evil spirits arrived, dragging their huge claws on the ground behind them. They noticed that the people that ate the fish had nice eyes, so they caused everyone who was asleep to go blind. The one who had tried to save his people hid in the roof of one of the houses. The evil spirits noticed that one person was missing, so they looked all around to find the hidden man. They could not find him, so they left; as they were walking away, the hidden man overhead one of them say, ‘The only way to harm us is to burn the tree by the agua jaula; the smoke will send us away.’ Eventually, all his people awoke to find out they could no longer see. They asked the man why they were blind, and he was not, but he replied, ‘I am blind like you, feel.’ Using a hollowed nut, the others began to feel the void and concluded that he was missing his eyes too. The man then rallied his people in order to beat the evil spirits that had taken their eyes. He gathered what he needed, guided his people back to the agua jaula, and burned the tree that the evil spirits lived in. All types of evil spirits fell out of the tree, men, women, children, old and young. But to the dismay of the blind group sitting on the burnt log of the tree, the evil spirits threw small nuts at their eyes, giving them back their eyesight, but in return, turning them all into giant river otters.”
It was a moment of true cultural exchange, and it was an honor to learn from such a wise and knowledgeable person.

As an educator, I believe experiences like this are crucial for helping all students understand and appreciate different cultures and ways of life. By immersing myself in the Amazon Rainforest and working alongside the Maijuna, I gained a deeper understanding of them as individual people and the challenges they face in preserving their way of life. From our neighbors next door to our tambo, Jairo (Hi-ro) and Marina, to Lenora, who cooked amazing meals (many others also made amazing food for us, including the leader of Sucusari Everest Ríos Vaca) to our forest guides and new friends Jeysen (Hay-sen) and Roller (Roy-yer), The journey through the Amazon felt like a family road trip. The road was the Sucusari River and the roadside attractions were the forest’s rich biodiversity greeting us at every bend.
I hope that by sharing my experiences with students and my community, I can inspire others to think critically about the world around them and to value the diverse cultures and traditions that make our world such a rich and fascinating place.