By Claire Lannoye-Hall, director of education for the Detroit Zoological Society (DZS).
Follow Claire on her journey through Peru when you read this blog on StoryMaps!
For more than two decades, the DZS has partnered with CONAPAC, a nonprofit organization in the heart of the Peruvian Amazon Rainforest. With the generous support of Amazon Explorama Lodges, a travel company with more than 50 years of commitment to the region, the partnership supports the conservation of this globally essential ecosystem. Each year, thousands of students and teachers receive school supplies, teachers participate in professional development workshops, and families have access to clean, safe drinking water.
In addition to the partnership’s commitment to education and safe drinking water, we support economic opportunities for interested communities. As part of this initiative, several thousand fruit trees have been planted in select communities as a source of added nutrition for families. As the trees mature and produce excess harvest, fruits are sold as a source of income.

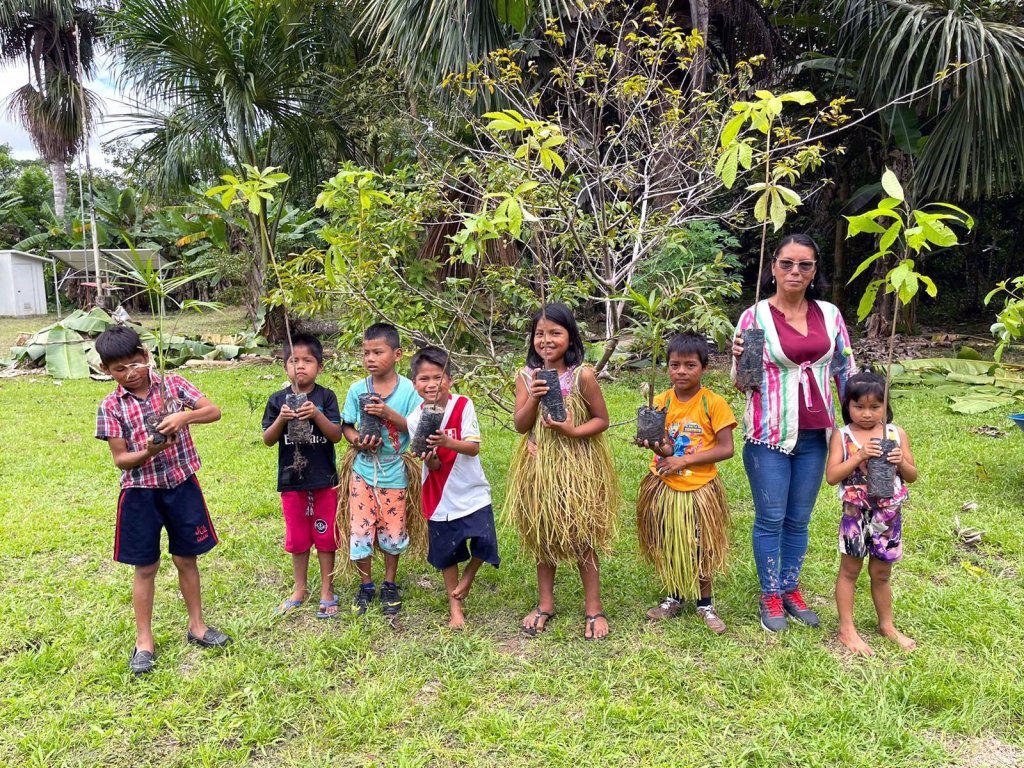
During the first week of December 2023, four team members from the Detroit Zoo traveled down to Peru to participate in fruit tree planting. The Fruit Tree Planting Foundation provided funding for fruit trees that are native to the Amazon rainforest to be grown and transported. Pedro Paurcarcaja, an arborist in Iquitos, Peru, grew the trees from cuttings and seeds. Each tree was cared for and allowed to grow to a size that could be successfully transplanted. The trees were then placed in crates by type and transported down the Amazon and Napo Rivers on a cargo barge. Thousands of trees were delivered to the designated communities.
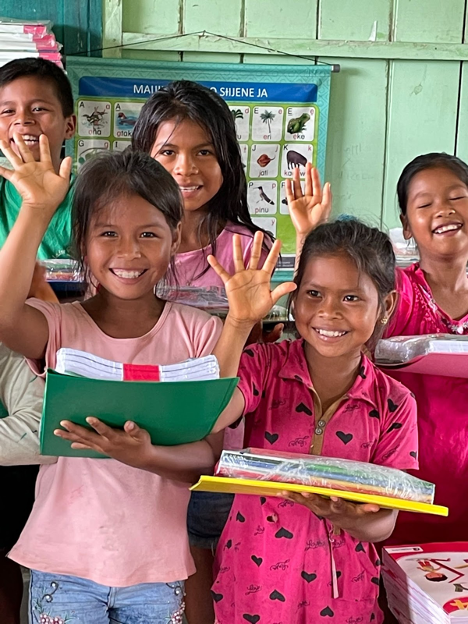
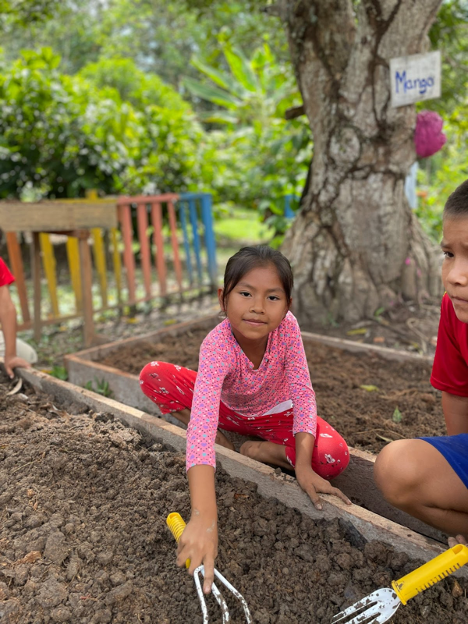
Each morning, we joined a group of volunteers and representatives from the Fruit Tree Planting Foundation, CONAPAC staff and an experienced guide and translator from Explorama. We all took a boat to reach the designated community. Some of the trees went to individual families who expressed their interest and commitment to growing trees on land they have available. The families were responsible for planting their trees. Several hundred additional trees were planted in community spaces and for the schools.
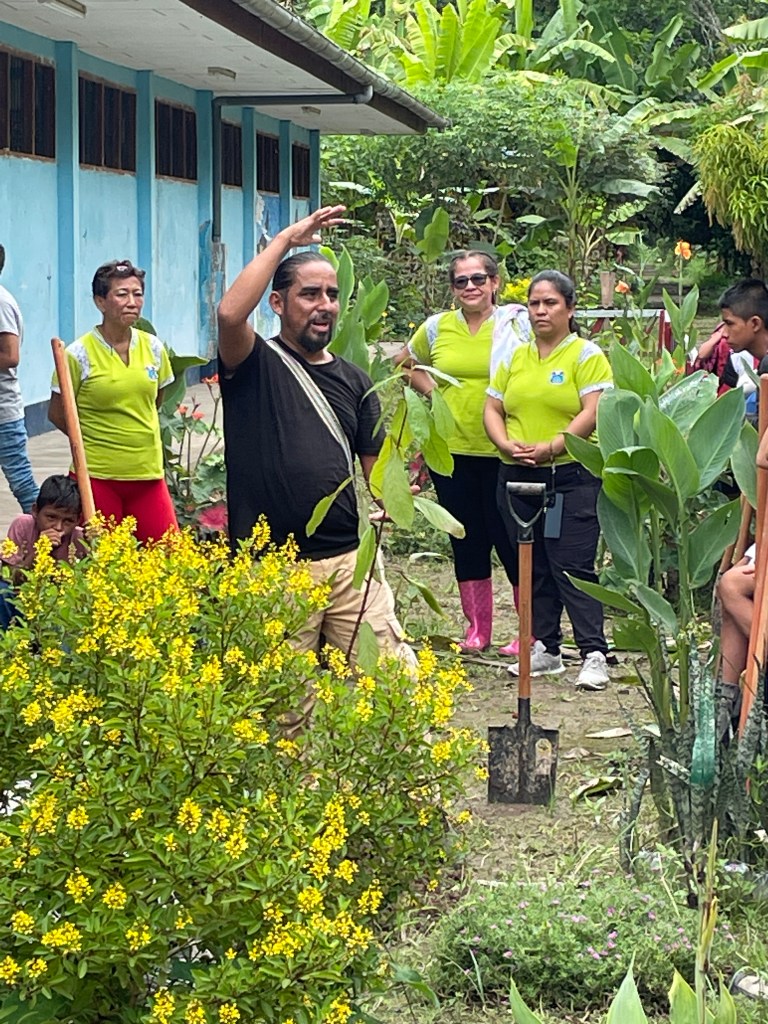

Before our arrival, the communities prepared areas previously used for agriculture, such as corn and banana palms. With shovels and post-hole diggers in hand, the FTPF representative carefully demonstrated how to plant the saplings to ensure they had the best chance of surviving. We worked alongside members of the community, especially the children, and planted the trees designated for the community and school areas. The planting wrapped up each morning shortly before lunchtime. Spending several hours at each community provided opportunities to learn each other’s names, communicate in various forms (even if it was just smiles!), and gain a glimpse into the day-to-day life of our partners.
For the final two days, we visited an additional community in the afternoon. Both communities planted trees several years ago through the FTPF initiative and proudly showed us the trees’ growth. Ramon Castilla shared with us that more than 90 percent of their trees had survived, which is an impressive feat considering the risk of insect and flooding damage. Their success was a testament to the trees being planted in the right areas and their commitment to caring for them. The community of Jorge Chavez treated us to fruit fresh off the trees, including papaya and star fruit.
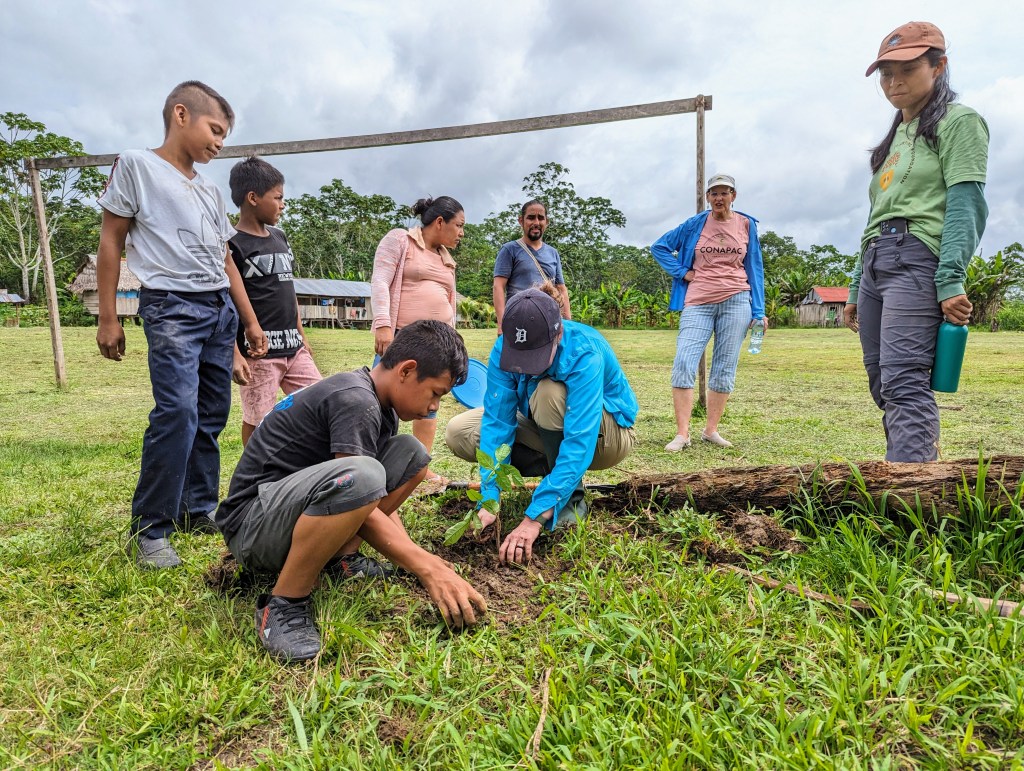

The community visits were also an opportunity to check in on the water purification systems, ensuring things were working correctly and the communities had access to safe, clean drinking water. For more information about CONAPAC’s clean water programming, click here.
Conservation work, especially when conducted in international settings, often does not address the needs or fundamental rights of the people who are directly impacted by laws and regulations that are put in place in the spirit of protecting animals and natural resources. While time-consuming, building meaningful relationships with individuals and communities who live adjacent to or share the same space as essential conservation areas can create vitally important allies. To do this well takes time and an investment in the wealth of knowledge and expertise of individuals who have lived for generations in the conservation areas. This partnership exemplifies the benefits of what collaborative conservation can accomplish.
To contribute to the vital conservation work in the Amazon rainforest, click here.